Today, utility transmission and distribution are experiencing a major shift towards digitality, automation, and enhanced collaboration, pushing boundaries towards advanced technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), and Extended Reality (XR). All these technologies provide innovative solutions to the utility sector, enhancing companies’ asset and operation efficiency, improving workforce experience, and uncovering new revenue streams.
Technologies Used by Utilities
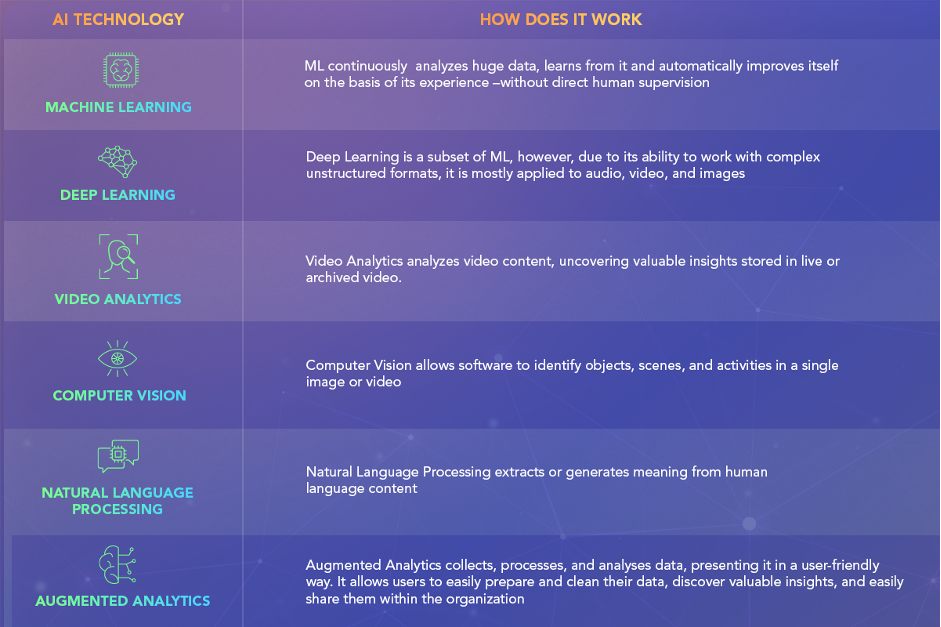
Artificial Intelligence
AI refers to the field of computer science that provides a system that performs human-like tasks, such as speech and text recognition, learning, and problem-solving. AI involves a set of various technologies. Depending on the purpose, environment, and technology stack, one or the other technology may be applied in the utilities. For instance, Computer Vision can be used to provide data classification for employees. Natural Language Processing (NLP) offers virtual assistants and chatbots for both customers and the workforce. Below is a brief overview of AI technologies.
IoT refers to the network of interrelated computing objects, devices, and sensors that interact and exchange huge sets of data over the internet. Real-time data exchange processed by the IoT software allows to reduce costly downtime, increase operational efficiency, enhance safety on the premises, as well as boost company performance.
McKinsey Global Institute’s research indicates that IoT has the potential to attract $11.1T by 2025.
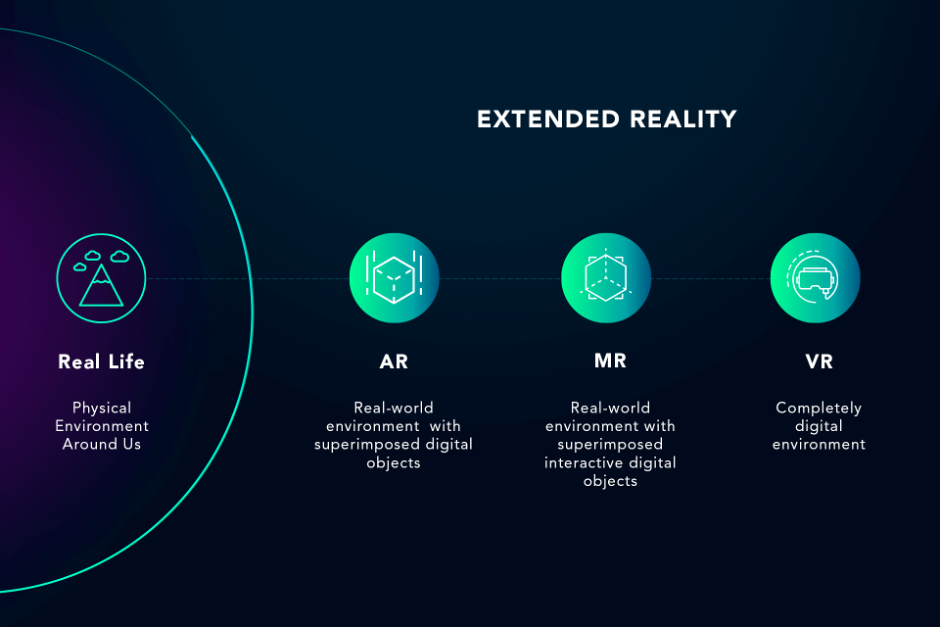
Extended Reality
XR is generally referred to as a set of technologies, namely Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR). All of them reflect artificially created reality that differs only in the immersion degree.
The Accenture Technology Vision 2018 report shows that, worldwide, 52% of enterprises already develop their own XR strategies and 79% believe that, over the next three years, XR will reach a broad, cross-industry impact.
Internet of Things in Utilities
IoT, with its connecting capabilities and ability to process Big Data, found a major role in the utility segment, streamlining costs through optimizing operating inefficiency. According to MarketsandMarkets, a global market research company, the total IoT market size particularly in utility of about USD 28.6 billion in 2019 is expected to hit USD 53.8 billion by 2024, growing at a CARG of 13.5%.
Using IoT in utilities improves efficiency, generates new revenue, and conserves enterprise resources. IoT-powered sensors can optimize gas and water production and distribution, helping utility providers to keep up with the increasing demand from consumers. Moreover, an IoT system enhances workplace safety for utility workers. Examples of use cases follow:
Remote Asset Monitoring
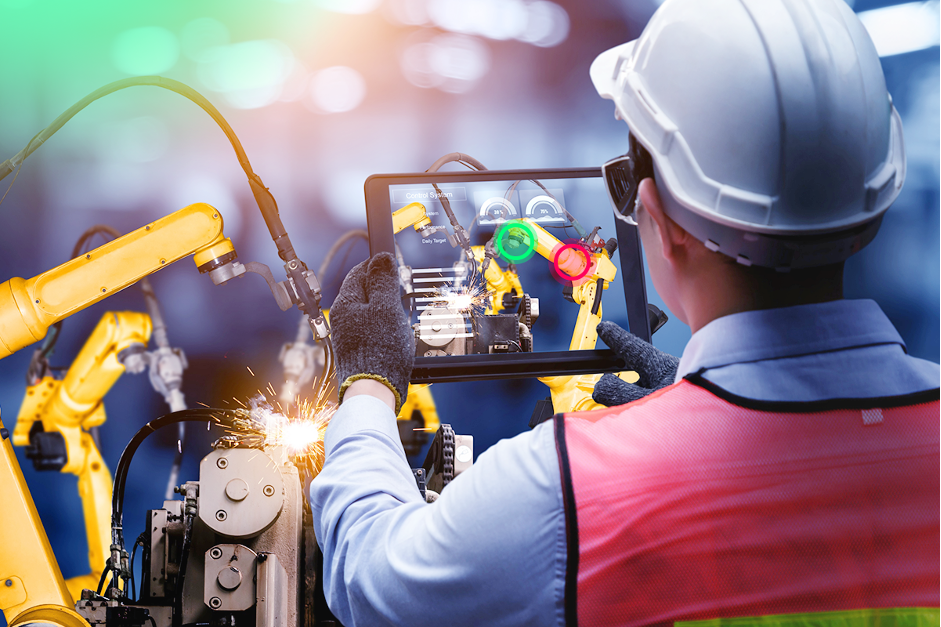
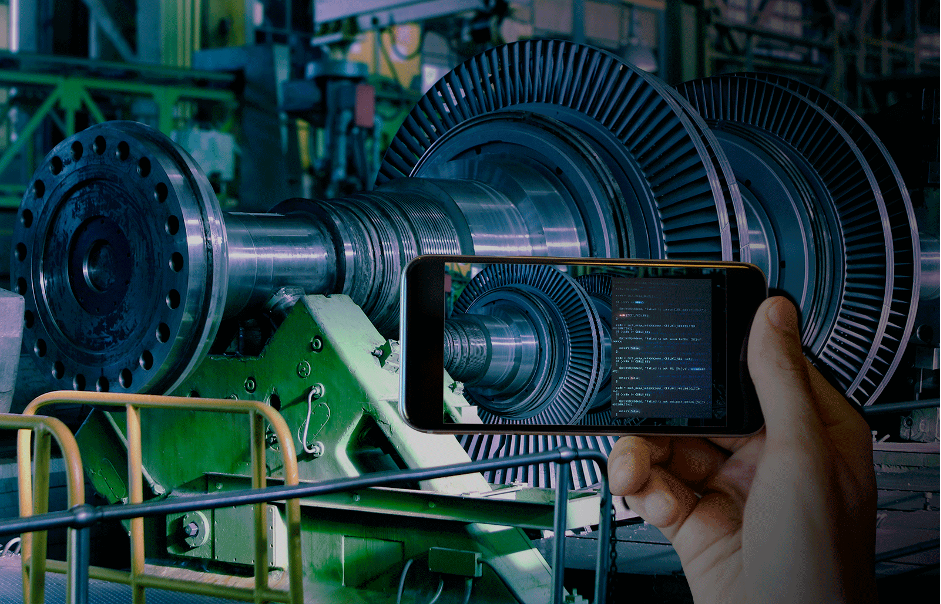
With IoT, utility companies can track and manage assets more efficiently. Connected IoT sensors, embedded in assets, are able to measure wear, vibration, tear, temperature, etc. to estimate the overall state of assets from turbines to transmission lines. The system also provides real-time alerts, predictive analytics, and automatic reports. As a result, the application users can constantly monitor assets, identifying any failure promptly or even before it occurs.
Smart Consumption/Smart Metering
Smart meters are increasingly deployed in electricity distribution grids worldwide, but also on gas and water grids as well. With IoT, utilities can provide the opportunity to be energy-efficient to their consumers. With IoT-powered smart meters, internet-connected devices that share data on electricity consumption with a utility company, consumers can make smart decisions regarding electricity usage and take appropriate steps to tune theirs to respond to electricity market price signals, or to postpone consumption when spare generation capacities are running thin.
For instance, Softengi has developed a Smart Electricity Meter for Aziot, which is now deployed in more the 200 apartments. Tenants install a small device, which in real-time tracks the amount of consumed electricity. Softengi has also designed a similar application, a Smart Metering System, for a water utility. It is an information-analytical system for data collection and processing, which allows the company’s inspectors to easily read meters installed around the city with mobile devices.
IoT for PPE & Employee Health Monitoring
The Covid-19 outbreak has forced enterprises to reconsider their work practices and adjust them to the current situation. Because of the pandemic, the industry has been subjected to many limitations related to workers’ distance maintenance, employee health monitoring, and remote working. However, IoT, with its tracking capabilities, allowed companies to easily comply to the posed restrictions. For instance, by embedding employees’ wear with sensors, utility companies can monitor their workforce health state. Remote monitoring of human health indicators (temperature, pulse, pressure) with portable IoT devices enables utilities to better care for their workers. Moreover, the IoT system can track Protective Personal Equipment (PPE) compliance, if the wear is worn appropriately and has no damage.
Extended Reality (XR) in Utilities
XR, which involves Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR), is the technology, which can significantly enhance the utility business. Innovating and automating many operational processes, XR allows companies to reach a new level in their business and be competitive in today’s volatile market.
Digital Twins
“Digital twins are becoming a business imperative, covering the entire lifecycle of an asset or process and forming the foundation for connected products and services. Companies that fail to respond will be left behind.”- Thomas Kaiser, SAP Senior Vice President of IoT
Digital Twin is a relatively new concept that has already gained a lot of attention across different sectors, including Utilities. A Digital Twin is a virtual replica of a real-world asset, which is achieved due to continuous data transmission, which allows the virtual object to exist simultaneously with the physical one. For example, Softengi has developed a digital twin for facility monitoring was modelled from BIM for a French company. Due to real-time data obtained from IoT sensors, an interactive 3D replica of a facility is continually updated, users interact with the digital twins via smartphones or laptops as a facility digital twin is available for both web and mobile apps.
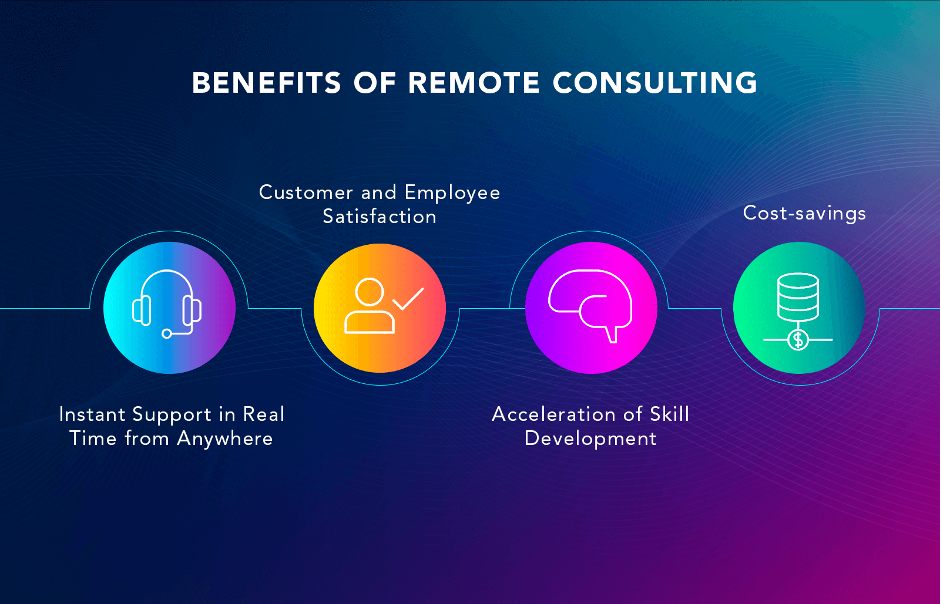
Remote Assistance
With AR, assets can be maintained more effectively. AR-powered remote consulting allows experts who are not present on-site, guide inexperienced employees remotely in real-time. This kind of remote assistance can be especially useful in complex equipment verification and repair. As a result, companies can lower expenses on subject matter experts (SME), as they can guide junior employees in complex operations, thereby avoiding operational errors. Moreover. AR-driven remote assistance will allow companies to keep retired workers, providing them with the possibility to work remotely.
Virtual Reality/ Augmented Reality Training for Specialists
The most significant problem in the utility sector is the aging of the workforce, which leads to the loss of expert knowledge. According to a report provided by the US Department of Energy, 25% of US employees in electric and natural gas utilities are going to retire during the next five years. Moreover, according to a survey of the U.S. Department of Energy, 72 percent of energy employers complain about the shortage of qualified staff.
With the outbreak of coronavirus, utility companies have to adjust to the government restrictions imposed during the pandemic. In some cases, companies cannot send enough experts to support maintenance operations, and have to delegate this work to less qualified employees.
AR, with its remote consulting capabilities and ability to simulate various scenarios in the working environment, can meet this challenge, allowing companies to educate their employees more easily. For instance, AR improves learning processes by overlaying virtual objects, such as images and videos on the surrounding environment. As a result, utility employees can get anything they need right in their field of vision, thereby getting a better understanding of the equipment and operational processes. With AR, energy, and utility companies significantly improve their training programs, as well as prepare the highly qualified workforce.
Artificial Intelligence
AI is the technology that revolutionizes almost every industry. IDC predicts that spending on AI systems will grow annually and in 2022 reach $79.2 billion. In high-complex and asset-intense segments as utilities, AI has become a must-have tool to operate efficiently and stay competitive. Especially in a COVID-paced world, where on-site workers are constantly reduced because of resources shortage, AI can be a lifeline to keep most employees by enabling successful remote work, which, as a result, is more efficient and cost-effective.
According to the PwC Consumer Intelligence Series 2017, a consumer-focused research, 54 percent of business executives say that their adoption of AI within the workplace has led to a boost in productivity. Examples of applications of AI in Utilities follow:
Load Forecasting
Demand forecasts are vital for utilities. AI-powered load forecasts allow utility companies to make timely adjustments, allowing them to operate more efficiently. Softengi applies machine learning technology, enriching it with external datasets to forecast short- and long-term customers’ demand. AI load forecasting enables energy providers to develop informed and data-driven strategies based on real-time reposts on current and future energy consumption.
Ilya Gandzeychuk, a Chief Technology Officer in Softengi, says: “AI enables utility companies to better adjust to the shifted daily and weekly power loads. Applying AI systems allows forecasting short and long-term loads, predicting supply and demand in real-time.”
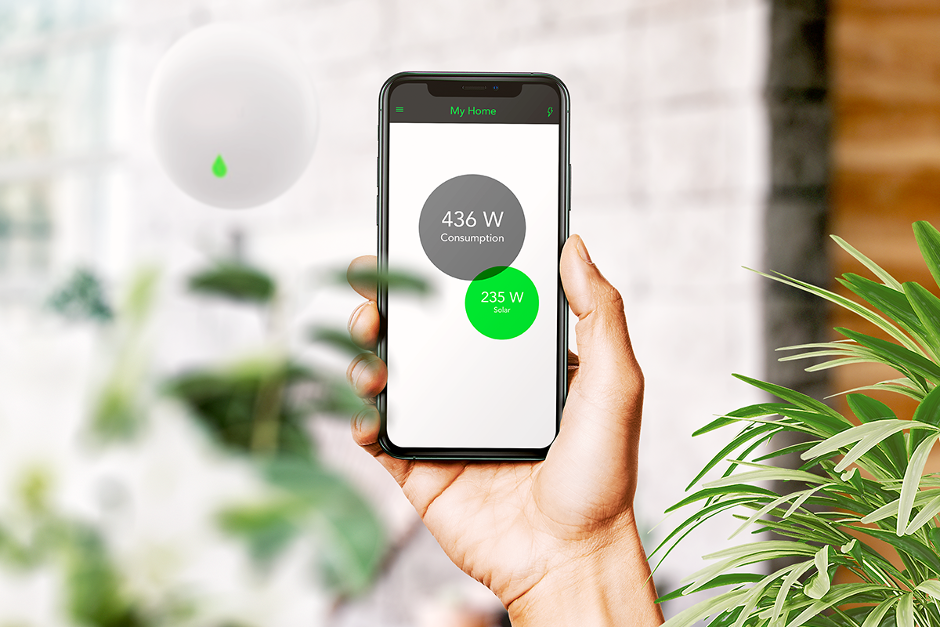
Smart Home Energy
A smart home system based on AI is a cutting-edge trend in the consumer world. AI, with Machine Learningtechnology, can teach users how to consume energy smartly and be energy-savvy, thereby cutting costs, reducing wastage, as well as improving convenience. The system learns householders’ consumption patterns and then makes suggestions on how to optimize energy usage.
Customer Insights
Natural Language Processing (NLP), a subfield of AI, which allows AI to recognize and process human language, can analyze the constant flow of customer data, for instance FAQ, feedback from satisfaction surveys, social media activity, etc., learning their behavior and preferences. As a result, utilities can better understand their clients, adjust prices, and provide better services. Moreover, AI can develop tailored offerings for particular customers to retain them.